XPath(XML/HTML Path Language)通过“路径表达式” 在 XML/HTML 中选择节点。
什么是路径表达式?
由节点,限定符构成的能选择节点集合的表达式。
节点
- 标签节点 (XML/HTML 标签,如 div, tr, td 等)
- 文本节点, (一般在最后最底层,字符串类型了,如属性 @class,文本 text(), 注释 comment())
- 特殊节点(如
.表示当前节点,..表示父节点)
限定符
//# 限定范围为所有后代节点/# 限定范围为子节点[]# 限定范围为当前节点Axe::# 限定范围为轴相邻节点,如兄弟,最近的祖先,最近的子孙等
使用方式
Chrome Elements

Chrome Console
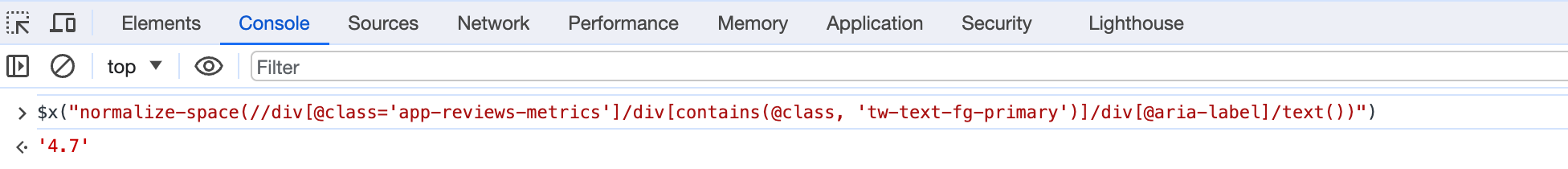
Scrapy shell
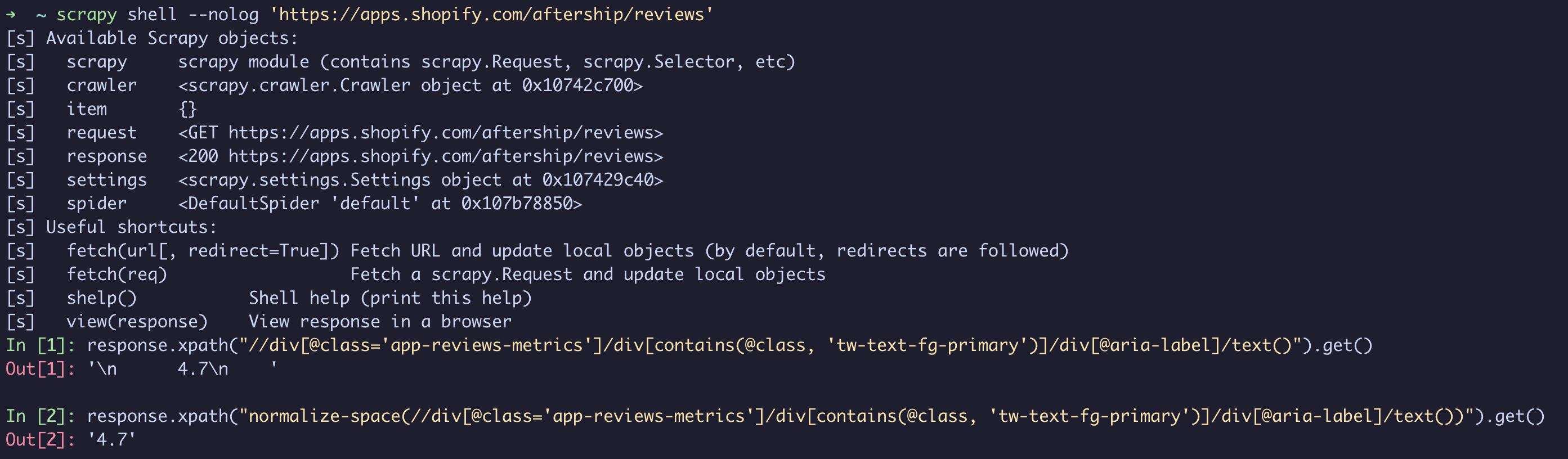
案例
//ul/li/a
# 所有 ul 节点,下一节点为 li,且 li 下一节点为 a 的 a 标签节点集合
//button/text()[.=‘Submit’]
# 所有 button 节点, 下一节点为 text() 结点,且该结点的内容为 'Submit' 的 文本节点集合
//a[@id=“abc”][@for=“xyz”]
# 所有 a 节点,且该节点的 id 属性结点内容为 abc, 且该节点的 for 属性结点内容为 xyz 的 a 标签集合
# 使用 [][] 进行了多重且限定,与 //a[@id="abc" and @for="xyz"] 等价
//a[@name or @href]
# 所有 a 节点,且该节点有 name 属性结点或者有 href 属性结点的 a 标签结点集合
# 使用 or 进行了多重或限定
//a[starts-with(@href, “/”)]
# 所有 a 节点,且该节点的 href 属性以 / 开头的 a 标签集合,
# //a[starts-with(./@href, “/”)] 中的 ./ 表示当前节点, 也可以省略
//a[contains(@href, ”https“)]
# 所有 a 节点,且该节点的 href 属性包含 https 的 a 标签集合
//ul[count(li) > 2 and li[ends-with(@class, “active”)]]
# 所有 ul 节点,且该节点下的 li 节点数量大于 2 且 li 节点的 class 属性结点以 active 结尾的 ul 标签集合
# 使用了 count() 函数,且使用了 ends-with() 函数
# 使用了 [[]] 进行了多层嵌入式限定
//ul/li[last()]
# 所有 ul 节点,且该节点下的最后一个 li 节点的 li 标签集合
//h1/following-sibling::ul
# 所有 h1 节点,且该节点的下一个兄弟节点为 ul 的 ul 标签集合
# 使用了 following-sibling:: 轴
//div[@class='col-9 col-md-10'][count(./div)=2] | //div[@class='col-10 col-md-11'][count(./div)=2]
# 使用了 "|" 对路径表达式进行了联合,会返回满足第一个及第二个的 div 合集
经验
text() 也是结点,可以使用[](专门名词为谓语动词 predicate)进行限定(过滤选择)。
[] 是可以联结的(Chainable:
[][]), 也是可以嵌套的(Nestable:[[]])。路径表达式可以通过 “|” 获取合集。
浏览器 F12 即可以执行 Xpath 表达式,在代码里需要注意
tbody标签是否存在于 source code。你还可以在 Chrome Console 中执行如
$x("//strong[contains(text(), ‘Order #’)]/parent::td/text()[re:match(., ‘W\d{14}’)]")的表达式,它结合了 re 的功能。善用函数如
substring-before(XPath, "split_str")可以只获取选择到的 text 的某一部分,而没有必要对表达式返回的结果再进一步处理,一部到位就好了, 还有如concat(XPath, XPath)可以连接 2 个 XPath 的内容,当然在执行时也需要在 Chrome Console 中执行。在遍历某些结点时,要明白它是一个引用,也就是说,你还是可以遍历到它的前后节点(following, preceding),父节点(../),甚至根结点(得以相对路径不断向上寻找)。
如果你使用的是 Python 语言,可以尝试下 parsel 这个库,它的链接是 https://parsel.readthedocs.io/en/latest/usage.html#learning-expression-languages ,而且它现在还支持 JMESPath,即对 JSON 类型数据选择与过滤,功能很是强大,还有些链接也很有启发,如 XPath cheatsheet: https://devhints.io/xpath 给了很多常用的案例,还有 XPath tips: https://www.zyte.com/blog/xpath-tips-from-the-web-scraping-trenches/ 给了些有用的经验,并且还能知道 »>
Avoid using contains(.//text(), 'search text') in your XPath conditions., 这点非常有趣。如果是 XML 类型,需要声明 namespace,如
//ns:div[@class='col-9 col-md-10'],其中 ns 是 namespace 的简写,而且需要在代码中声明,如namespaces = {'ns': 'http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml'},这样就可以使用了。
函数参考
Node functions
name()
text()
lang(str)
namespace-uri()
count()
position()
Boolean functions
not(expr)
String functions
contains()
starts-with()
ends-with()
concat(x,y)
substring(str, start, len)
substring-before(‘01/02’, ‘/’)
substring-after(‘01/02’, ‘/’)
translate()
normalize-space()
string-length()
Type conversion
string()
number()
boolean()
Axe 轴参考
ancestor
ancestor-or-self
attribute
child
descendant
descendant-or-self
namespace
following
following-sibling
preceding
preceding-sibling